Ultrasound
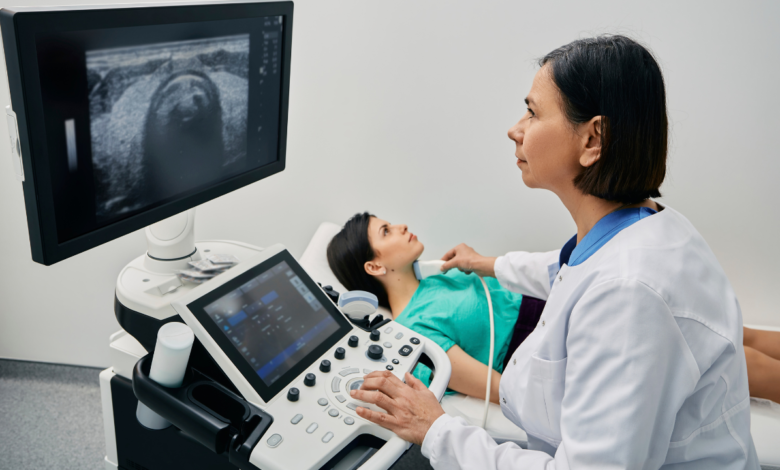
What is ultrasound?
Ultrasound is a medical imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of organs and tissues inside the body.
These sound waves bounce off different tissues in the body and return to the machine, which then creates a picture.
Why ultrasound is required?
Ultrasound is a valuable diagnostic tool for many reasons:
- Non-invasive: It does not involve radiation, making it safe for most individuals, including pregnant women.
- Versatile: Ultrasound can be used to examine various organs and tissues, including the heart, liver, kidneys, pancreas, and reproductive organs.
- Real-time imaging: Ultrasound provides real-time images, allowing doctors to observe the movement of organs and structures.
- Painless: The procedure is generally painless and does not require any special preparation.
which are the method of ultrasound?
Methods of ultrasound:
- 2D ultrasound: This is the most common type of ultrasound, providing a two-dimensional image of the organ or tissue being examined.
- 3D ultrasound: Creates a three-dimensional image, offering a more detailed view of structures.
- 4D ultrasound: Similar to 3D, but with the added benefit of real-time movement, allowing visualization of fetal movements or heart function.
- Doppler ultrasound: Measures blood flow through blood vessels. This is particularly useful for assessing conditions like heart disease or blood clots.
who should go for ultrasound?
Many individuals may benefit from an ultrasound, including:
- Pregnant women: To monitor fetal development, detect abnormalities, and assess the placenta.
- Patients with abdominal or pelvic pain: To identify the cause of pain, such as gallstones or ovarian cysts.
- Individuals with heart conditions: To evaluate heart function and detect abnormalities.
- Those with suspected vascular diseases: To assess blood flow in arteries and veins.
- People with thyroid or kidney problems: To evaluate the size and function of these organs.
What are the results of ultrasound?
Results of ultrasound:
Ultrasound results can vary depending on the specific condition being evaluated. However, common findings may include:
- Normal anatomy: The organs and tissues appear healthy and without any abnormalities.
- Abnormalities: The ultrasound may reveal cysts, tumors, masses, or other structural changes.
- Functional issues: Ultrasound can assess the function of organs, such as blood flow through the heart or the movement of the intestines.
What are the components of ultrasound?
Components of ultrasound:
A typical ultrasound setup includes:
- Ultrasound machine: This is the main component that generates and receives sound waves and creates images.
- Transducer: A handheld device that emits and receives sound waves. The type of transducer used depends on the area being examined.
- Gel: A conductive gel is applied to the skin to ensure efficient transmission of sound waves.
- Monitor: A screen that displays the ultrasound images.
By providing valuable information about the internal structures of the body, ultrasound plays a crucial role in diagnosing and monitoring various medical conditions.